The use of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to significant shifts across various industries, with banking emerging as a prominent adopter. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated digital transformation, compelling banks to adopt AI technologies to meet the growing demands for digital banking services and remote access. As banks face increased competition and changing consumer preferences, the adoption of AI technologies has become essential for their ongoing viability and progress. The significance of AI in banking lies in its ability to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer engagement, and enable informed decision-making through data analysis. Traditionally, the banking sector relied heavily on manual processes, but the transition to AI marks a crucial step towards automation and modernization.

The rise of digital banking solutions and the rapid increase in data from customer transactions have encouraged banks to incorporate AI into their systems. Key drivers of this shift include the need for real-time processing, the demand for personalized customer experiences, and the necessity for effective risk management—all of which motivate financial institutions to utilize AI for a competitive advantage in a rapidly changing environment.
Therefore, for the comprehensive analysis, drawing on empirical data from recent studies, this report explores the AI’s significance in banking, focusing on its impact on customer service, operational efficiencies, and profitability, while addressing the limitations and ethical considerations inherent in its implementation. By reviewing how AI is remaking service to clients, improving operations, and increasing profitability, this analysis highlights the importance of adopting a balanced strategy that capitalizes on AI’s potential while addressing its limitations. Banks can fully realize the potential of AI to drive growth,
innovation, and client trust in an increasingly digitized financial sector by implementing innovative leadership and ethical governance.
The influence of artificial intelligence on customer service within banking has been profound, offering enhanced accessibility, efficiency, and personalization. AI-powered tools, especially chatbots and virtual assistants, are becoming integral to customer service, providing around the clock availability and managing high volumes of routine inquiries for automated responses to a large volume of routine inquiries. These AI tools ease the workload for bank employees, allowing them to focus on more complex tasks, while also ensuring customers receive faster and more satisfying responses. By leveraging AI, banks can analyze customer data to offer personalized services that foster stronger connections and encourage loyalty. Innovations such as voice assistants, biometric solutions, and machine learning enhance the customer journey at every stage, from onboarding to after-service support. AI’s ability to anticipate customer needs and deliver proactive solutions not only improves relationships but also streamlines operational efficiency (Fares et al., 2023). This is considered further by the research in
the Indian banking sector carried by (Shaikh et al., 2024), claims that 63% of surveyed customers preferred AI-driven tools for basic services, such as balance inquiry and transaction histories. This shift is happening globally, showing the increased dependence on AI to meet customers’ needs quickly, efficiently, and with high satisfaction rates.
Further, studies argue that AI-enabled chatbots and virtual assistants are effective in retaining customer engagement. A 24.7% increase in customer re-engagement has been observed in banks utilizing AI chatbots, affirming AI’s potential in fostering customer loyalty through timely and personalized responses (Bhattacharya & Sinha, 2022).

Another benefit AI provides in the banking sector is Personalization. AI algorithms analyze customer data to deliver customized financial advice, services, and product recommendations, which enhance customer relationships. For instance, machine learning algorithms allow banks to provide tailored recommendations based on customer spending patterns and historical behavior (Kreger, 2023). This individualized approach strengthens customer loyalty, highlighting the strategic importance of AI for enhancing customer service. Additionally, AI is reshaping how banks interact with customers by offering highly personalized experiences through tools like chatbots and robo-advisors (Almustafa et al., 2023 para. 8). These technologies learn from customer behavior to provide tailored advice and solutions in real-time, making banking more accessible and efficient. By handling routine queries and offering insights into spending patterns, AI not only improves service speed but also builds trust and financial awareness among users.
Another advantage of adopting AI is its significant contribution to operational efficiency, especially in automating repetitive tasks and improving practices of risk management. A detailed study by (Baffour Gyau et al., 2024) across 20 countries found that AI integration within banking operations reduced operational costs by 15-20%, largely due to the automation of back-office tasks such as compliance monitoring, fraud detection, and data entry. Machine learning models now play a pivotal role in fraud detection by analyzing vast datasets to detect unusual patterns with far greater precision than conventional methods. Consequently, AI not only optimizes daily operations but also helps minimize
financial losses due to fraud, thereby bolstering the operational integrity and resilience of financial institutions (Forging New Frontiers, 2020). AI has also demonstrated a measurable impact on profitability in the banking sector, particularly through its application in lending processes. The use of predictive models and algorithms enables banks to assess creditworthiness accurately, reducing the likelihood of non-performing loans (NPLs) and thereby improving return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE).
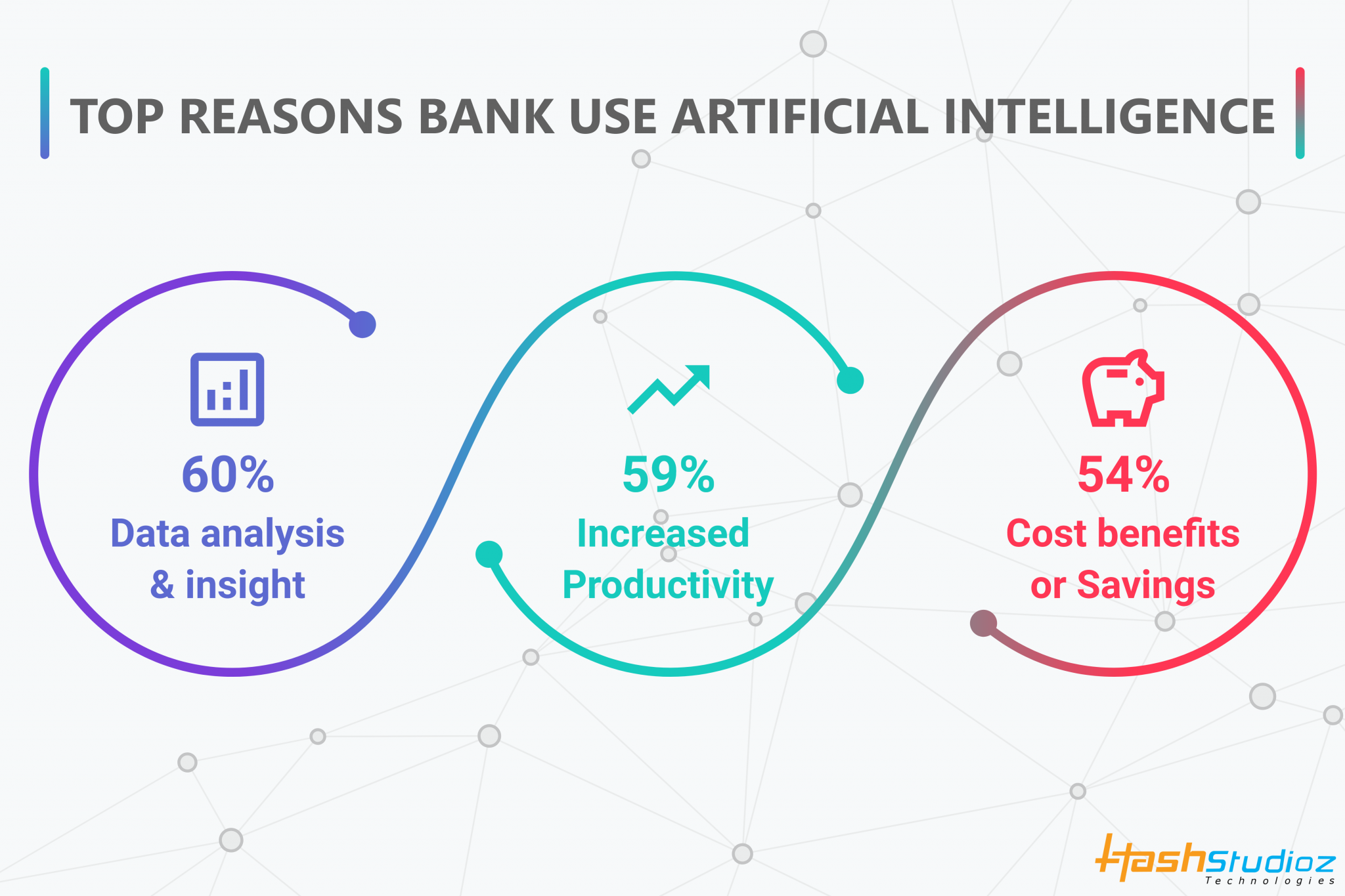
A study of (Baffour Gyau et al., 2024) claims that banks utilizing AI for credit assessment reported lower NPLs, reflecting a direct link between AI integration and profitability. AI driven credit models improve loan approval decisions by precisely evaluating credit risk, thereby mitigating the potential for loan defaults. The study of (Bhattacharya & Sinha, 2022) claims about McKinsey estimation of AI’s capacity that can increase value by $1 trillion annually to entire banking sector across the globe, largely by improving service customization and efficiency in the operational activities. In emerging markets, such as
Pakistan, banks that have strategically invested in AI have reported markedimprovements in financial performance, underscoring AI’s capacity to drive profitability in various economic environments (“The Impact of Investment in AI on Bank Performance,” 2024). Moreover, AI is streamlining banking operations by automating routine processes and improving decision-making in areas like credit risk management and market analysis. With predictive tools, banks can identify risks early and make smarter financial decisions. Tasks like compliance monitoring and forecasting are faster and more accurate with AI, reducing errors and saving time. While larger banks thrive on these benefits, smaller institutions often struggle with the high costs of adopting AI. Collaborations or outsourcing AI solutions could help level the playing field, making these advanced tools accessible to more players in the financial industry (Almustafa et al., 2023).
Despite these positive outcomes, the integration of AI in banking poses certain challenges and limitations. A significant barrier to rapid AI adoption is the substantial financial investment required to implement and maintain AI infrastructure, a cost that can be prohibitive for smaller financial institutions. Further to this, a study (Baffour Gyau et al., 2024) claims that AI system implementation and annual maintenance costs can exceed $1 million, making it difficult for smaller banks to remain competitive in AI-driven innovation Additionally, the need for skilled technical personnel to manage AI systems presents a challenge, particularly in regions with limited access to specialized talent. Moreover, effective personalization requires extensive and reliable data, which smaller banks may find challenging due to limited financial and technological resources.
In addition, protecting customer data, ensuring privacy, and maintaining transparency in AI-driven decisions are often known as critical challenges. Legacy systems in banks usually require costly upgrades to integrate AI effectively, and smaller institutions find these investments daunting. Additionally, finding skilled professionals to manage AI systems is a growing issue. Banks need to strike a balance, using AI where it excels while keeping human oversight in areas where technology falls short. Investing in training and fostering partnerships can help address these challenges and support smoother adoption.
Also, balancing AI with human expertise remains critical for addressing complex services needs and ensuring comprehensive customer support (Almustafa et al., 2023).
Similarly, ethical considerations on data privacy and algorithmic bias further complicate AI’s role in banking. AI systems rely on extensive data for functionality, which raises concerns about privacy and the potential misuse of customer information. (Payette & Torrie, 2020) highlight the critical importance of robust AI governance frameworks to ensure that banks uphold transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI-driven decisions. Another concern that has been brought up in AI is algorithmic bias. It means, AI models may inadvertently perpetuate discrimination as they are trained on historical data, particularly in credit decisions. Instances of AI-driven credit models producing disparate outcomes for individuals with similar profiles underscore the necessity for rigorous oversight to prevent biased practices (Kreger, 2023). In Canada, for instance, banks have responded to these challenges by instituting fairness and accountability principles within their AI frameworks to protect customer rights and maintain trust (Payette & Torrie, 2024
On the other hand, technical challenges also arise when integrating AI with existing banking infrastructure. Most of banks are functioning on a kind of systems that are not compatible with modern AI solutions, necessitating costly and disruptive system upgrades. Research indicates that this integration process can lead to short-term inefficiencies and disruptions in service (Baffour Gyau et al., 2024). As such, banks must weigh the immediate costs and potential short-term setbacks of AI integration against the long-term benefits it promises. The success of AI in banking, therefore, requires a holistic approach that includes not only technical upgrades but also a strategy for minimizing disruptions and maximizing operational continuity.
Moreover, research indicates that while AI is effective for automating routine tasks, it may not fully replace the need for human interaction in certain banking services. A report of (Shaikh et al., 2024) depicts that 55% of banking customers prefer human assistance for complex issues, such as investment advice or loan consultations. This preference underscores the necessity of a hybrid approach that combines AI-driven efficiency with human expertise, especially for complex transactions that benefit from personalized, empathetic guidance. A blended model of service delivery, where AI handles routine inquiries while human advisors manage complex needs, may offer the most effective approach to customer service in the banking sector.
In conclusion, AI has transformed the banking industry by enhancing its service to customers, optimizing the operational costs, and increasing profitability. Through automated processes, fraud detection, and personalized customer interactions, AI enables banks to meet the growing expectations of digital-savvy customers and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly digitalized environment. However, the challenges related to algorithmic biases, high implementation costs, data privacy, technical integration need to be addressed more to authenticate sustainable and ethical AI adoption in banking. As banks continue to refine their AI strategies, the importance of robust governance frameworks and a balanced approach to human-AI collaboration will be crucial in realizing AI’s full potential and building trust within the sector. Moreover, AI is revolutionizing banking by making operations more efficient and customer interactions more personalized. It’s driving improvements in areas like credit risk management and process automation, giving banks an edge in a competitive market. However, adopting AI responsibly means addressing concerns like data security and costs while ensuring fairness and transparency in its use. By embracing ethical practices and fostering collaboration, banks can unlock AI’s full potential (Almustafa et al., 2023). This thoughtful approach will help the industry not only build trust but also sustain growth as it navigates an increasingly digital future
References:
Almustafa, E., Assaf, A., & Allahham, M. (2023). IMPLEMENTATION OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR FINANCIAL PROCESS INNOVATION OF COMMERCIAL BANKS. [IMPLEMENTAÇÃO DE INTELIGÊNCIA ARTIFICIAL PARA PROCESSO FINANCEIRO INOVAÇÃO DE BANCOS COMERCIAIS] Revista De
Gestão Social e Ambiental, 17(9), 1-17. doi:Click Here
Baffour Gyau, E., Appiah, M., Gyamfi, B. A., Achie, T., & Naeem, M. A. (2024). Transforming banking: Examining the role of AI technology innovation in boosting banks financial performance. International Review of Financial Analysis, 96. Click Here
Bhattacharya, C., & Sinha, M. (2022). The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Banking for Leveraging Customer Experience. Australasian Accounting Business & Finance Journal, 16(5), 89–105. Click Here
Fares, O. H., Butt, I., & Lee, S. H. M. (2023). Utilization of artificial intelligence in the banking sector: A systematic literature review. Journal of Financial Services Marketing, 28(6), 835–852. Click here
Forging new frontiers: advanced technologies will revolutionise banking. (2020). Economist Impact – Perspectives. Click here
Kreger, A. (2023). Council Post: The Future Of AI In Banking. Forbes. click here
Payette, D., & Torrie, V. (2020). AI Governance in Canadian Banking: Fairness, Credit Models, and Equality Rights. Banking & Finance Law Review, 36(1), 5–38. Click here
Shaikh, A. A., Kumar, A., Mishra, A., & Elahi, Y. A. (2024). A study of customer satisfaction in using banking services through Artificial Intelligence (AI) in India. Public Administration and Policy, 27(2), 167–181. Click Here
The Impact of Investment in AI on Bank Performance: Empirical Evidence from Pakistan’s Banking Sector. (2024). KASBIT Business Journal, 17(1), 44–44. Click Here
Disclaimer: This report is part of my academic research.